With the advancement of technology, freeze-drying technology is becoming a household name, bringing convenience to more and more people. But what exactly is the working principle of a freeze-dryer? And how does it operate? Let’s dive into this mystery together.

The Working Principle of a Freeze-Dryer
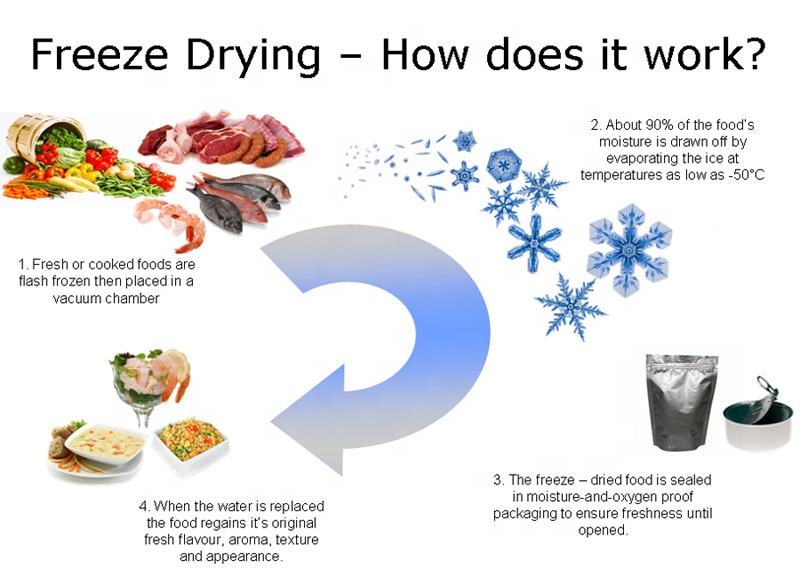
The core principle of a freeze-dryer is the direct sublimation of water from solid to vapor in a low-temperature vacuum environment, thereby removing moisture from the food. Thus, a freeze-dryer first freezes the food, then extracts the air around it, and gradually raises the temperature in a vacuum environment so that the ice sublimates directly into vapor. The vapor is collected by a condenser, effectively removing moisture and perfectly preserving the nutrients in the food.
The Freeze-Drying Process
Stage One: Freezing
This initial stage is crucial, rapidly freezing the food below the freezing point (typically between -30°C to -50°C) to form as small ice crystals as possible. This stage is critical to the freeze-drying effect as smaller ice crystals cause less damage to cell structures. After rapid freezing, both the texture and nutrients of the food are perfectly preserved.
Stage Two: Primary Drying
In this stage, by lowering the environmental pressure (using a vacuum pump) and gradually increasing the temperature, the ice crystals directly sublimate from solid to gas. At this time, the condenser in the freeze-dryer starts to operate, collecting sublimated vapor. This process can remove more than 95% of the water content from the food (in fact, our home freeze-dryers can remove more than 99.5% of the water content).
Stage Three: Secondary Drying
After primary drying, a small amount of moisture usually remains in the food, typically bound water within the food. The secondary drying stage slightly warms the food, further reducing the moisture content. This stage removes the vast majority of the remaining moisture.
Subsequent Packaging
After the freeze-drying process is complete, the food needs to be packaged immediately. To retain the quality of the food and extend its shelf life, it is recommended to use vacuum-sealed bags or sealed containers for packaging. The use of desiccants can enhance the effect.
Operating Environment
When using a home freeze-dryer, the vacuum pump will work for a long time, generating noise around 60 decibels. Therefore, it is necessary to find a suitable location for the vacuum pump to avoid noise pollution.
Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure the freeze-dryer operates efficiently and has a longer lifespan. This includes:
- Cleaning the Freeze-Dryer: Regularly clean the freeze-dryer, including the interior, trays, and exterior casing after each use. The interior of the freeze-drying chamber should be wiped down after each cycle.
- Checking and Replacing Vacuum Pump Oil: The vacuum pump is an essential component of the freeze-dryer and requires regular checks and oil changes. Refer to the user manual for specifics, as requirements vary by brand and model.
- Inspecting Seals and Door Gaskets: Regularly check the freeze-dryer’s seals to ensure they are in good condition and functioning correctly, with no wear or damage. Good seals are crucial for maintaining a vacuum environment during the freeze-drying process.
- Cleaning the Condenser: The condenser should be cleaned regularly to ensure freeze-drying efficiency. Ice accumulated in the condenser should be melted and removed after each freeze-drying cycle.

Applications of Freeze-Dryers
Freeze-dryers have a wide range of applications, significantly extending the shelf life of products without damaging their original structure and nutritional content.
Primary applications include:
- Food Preservation: This is perhaps the most well-known application of freeze-dryers. They can preserve a variety of foods, such as fruits, vegetables, meats, milk, and candies.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Freeze-drying technology is crucial in the pharmaceutical field for producing and preserving various drugs and bioproducts, like vaccines and antibiotics. Freeze-dried products can be stored at room temperature for extended periods while retaining their efficacy.
- Laboratories: Freeze-drying technology is also applied in laboratories for preserving samples, making them easier to store, transfer, and transport.
- Pet Food Manufacturing: Freeze-drying technology shines in the production of pet food, producing nutritionally rich pet food that pets particularly enjoy.
- Flower Processing: Freeze-drying technology is applied to preserve flowers and other ornamental plants, allowing them to maintain their natural color and appearance for extended periods, making them ideal for display.
- Cultural Heritage Preservation: Freeze-drying technology plays a significant role in the preservation of cultural heritage, especially for water-damaged books, documents, and other artifacts, preventing further damage.
The above is an introduction to the principles and applications of freeze-drying technology. Let’s further explore the use of freeze-dryers together:
Freeze-Dried Milk: A Nutritious And Healthy New Choice
How To Freeze-Dry Breast Milk At Home?
How Do You Freeze Dry Strawberries? A Guide To Freeze-Drying Strawberries
How Do You Make Freeze Dried Skittles?Freeze-Dried Skittles Making Guide
Are Freeze Dried Fruits Healthy?Let’s Hear The Professional Advice






