Lyophilization, or freeze-drying, is an important preservation technique widely used in food preservation, biopharmaceuticals, scientific experiments, and more. Lyophilization machines, based on freeze-drying technology, play an increasingly important role in today’s society. Let’s explore lyophilizers together.
What is Lyophilization? Is it the Same as Dehydration?
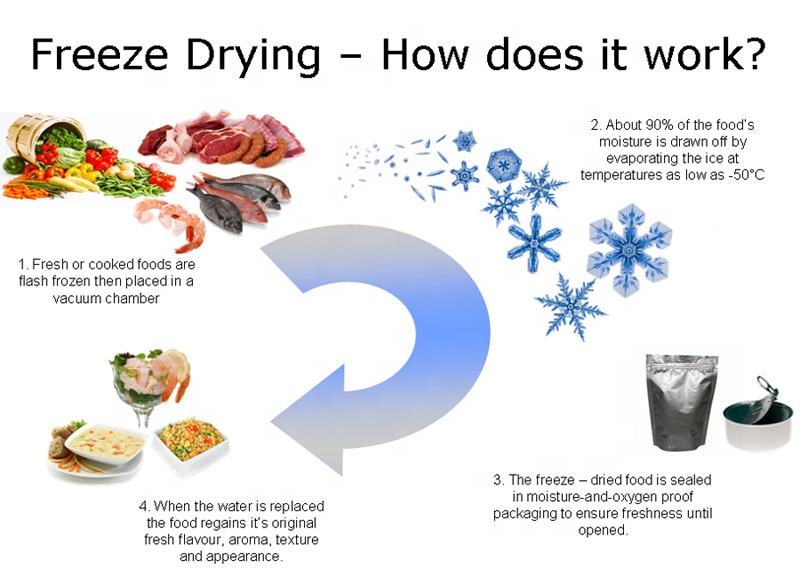
The principle of lyophilization is to freeze the liquid substance (water) and then allow the water to directly sublimate from solid to vapor in a vacuum environment. This process has two advantages that traditional techniques cannot match. Firstly, the lyophilization process is carried out at low temperatures, ensuring that the lyophilized food, medicine, etc., are not damaged, preserving their original flavors. Secondly, the lyophilization process only removes the water content from the substance without changing its characteristics, thus perfectly preserving the original properties of food, medicine, and other substances. In contrast, dehydration techniques are carried out at high temperatures, evaporating the liquid water through heat, which can alter the characteristics of the substance. Therefore, lyophilization technology has an irreplaceable advantage in food preservation and pharmaceutical experiments.
What Are the Types of Lyophilizers?
In terms of external dimensions, lyophilizers can be divided into tabletop household lyophilizers, medium-sized industrial lyophilizers, and large-scale industrial lyophilizers:
- Tabletop Lyophilizers: Mostly used in homes or laboratories, with small processing capacities, typically used for preparing small batches of freeze-dried foods.
- Medium-sized Industrial Lyophilizers: Suitable for medium-sized food processing plants or pharmaceutical manufacturers, with larger processing capacities for batch production of freeze-dried products.
- Large-scale Industrial Lyophilizers: Suitable for large food processing plants or pharmaceutical manufacturers, with even larger processing capacities for continuous production of large quantities of freeze-dried products.
What Are the Applications of Lyophilizers?
The application of lyophilizers is already very wide. It can be seen in various fields such as food processing, pharmaceutical engineering, biotechnology, scientific experiments, and more.
- Food Industry: Lyophilizers are used to process and prepare a variety of foods, which is the most common use of lyophilizers. This includes freeze-dried fruits, vegetables, meats, and even pet foods. We have detailed information on freeze-dried foods in this article: Freeze Dryer Recipes: Making Your Life Healthier.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: In the pharmaceutical industry, lyophilizers are used to prepare freeze-dried drugs. This preparation method can maintain the active ingredients of the drugs, extend the shelf life of the drugs, and make them easier to carry and use.
- Biotechnology: In the field of biotechnology, lyophilizers are often used to lyophilize cells, bacteria, and other biological samples. This method can preserve biological samples for a long time and maintain their activity to a certain extent.

What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Lyophilizers?
Lyophilizers have many advantages:
- Preservation of Original Characteristics: Foods or medicines processed by lyophilizers can retain their original characteristics. Even after long-term storage, they can be restored to their pre-lyophilized state simply by rehydration.
- Long Shelf Life: Freeze-dried foods can have an extremely long shelf life even at room temperature, which is a revolutionary breakthrough for some foods. For example, ice cream, which previously had to be refrigerated at low temperatures, can now be stored at room temperature after freeze-drying, which is great news for ice cream lovers without refrigeration conditions.
- Lightweight and Portable: Since lyophilizers remove all moisture from the food, they significantly reduce the weight and volume of the food. This is very beneficial for transportation and storage, especially outdoors, where freeze-dried foods can greatly reduce people’s burden.
- Convenient Consumption: Freeze-dried foods are very convenient to eat. They can be eaten directly or rehydrated to make the food fresh again. Freeze-dried foods are not only convenient but also nutritious and healthy, making them an ideal food in life.

These are the advantages of lyophilizers. So, what are the disadvantages of lyophilizers? Let’s take a look together.
- High Equipment Costs: Lyophilizers are expensive, especially industrial-grade lyophilizers, which start at tens of thousands of dollars. In comparison, household lyophilizers are much cheaper, costing only a few thousand dollars, but this is still a significant expense for ordinary families.
- High Energy Consumption: Lyophilizers consume a lot of energy. After purchasing a lyophilizer, the main cost is electricity. Industrial-grade lyophilizers consume a huge amount of electricity. In comparison, household lyophilizers have smaller power capacities, roughly similar to that of a hairdryer, so electricity costs are also within a controllable range.
- Long Production Cycle: Compared to other drying methods (such as dehydration), the lyophilization process takes a longer time. Depending on the shape, size, moisture content, and other factors of the food being lyophilized, the lyophilization time can range from several hours to several tens of hours.
These are the common issues with lyophilizers. If you are interested in lyophilizers and want to learn more, you can also read these articles for reference:
The Cube Freeze Dryer: Revolutionize Your Kitchen
Cheapest Freeze Dryer: Affordable And Effective
Is A Freeze Dryer And A Dehydrator The Same Thing?
Freeze Dryer For Home Use: How To Choose The Right Freeze Dryer






